
As long as an expense is considered ordinary and necessary, it can be reported to the IRS to help reduce tax liability.Īccording to the IRS, ordinary refers to expenses common to most business owners in the industry or trade.
#Variable expenses examples code
Guidelines for business expenses can be found in Section 162 of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC). These expenses will be subtracted from business revenue to show a company's net profit or loss and taxable income. They’re recorded on the income statement. Business expenses are recorded on an income (profit and loss) statement.Īlso referred to as deductions, business expenses are the costs of operating a business.Business expenses need to be considered ordinary and necessary for them to be tax-deductible.

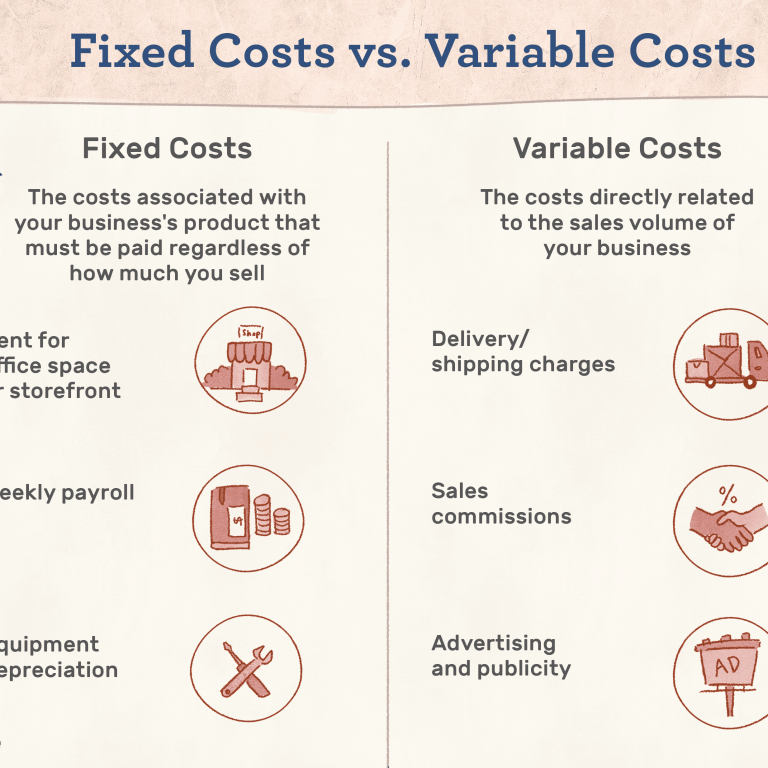
Tracking your business expenses helps you keep an eye on whether you’ll see profits or losses. You expect variable expenses each month, but the actual amount will vary. Some examples include sales commissions, gas for business vehicles and shipping costs. Variable expenses are expected, but they can change. Fixed expenses are regular and don’t change much - things like rent and insurance. Examples include inventory, payroll and rent. What Are Business Expenses?Īccording to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), business expenses are ordinary and necessary costs incurred to operate your business. It’s also crucial to understand what business expenses are and what you can deduct so you're not paying more taxes than necessary.

Meticulously tracking them ensures you know where your funds are going, and it helps you reduce your tax liability. East, Nordics and Other Regions (opens in new tab)Īny company will have business expenses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
